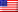
Europe’s Vega C rocket successfully deployed South Korea’s KOMPSAT-7 satellite into orbit on December 1st, marking a step forward in Earth observation capabilities. The launch, conducted from the Kourou Spaceport in French Guiana, placed the 3,990-pound spacecraft into a sun-synchronous orbit (SSO) approximately 358 miles above Earth.
What is a Sun-Synchronous Orbit?
SSOs are favored for Earth-observing satellites because they maintain a consistent lighting angle over target areas. This means images captured at the same time of day will have uniform illumination, crucial for accurate data analysis and comparisons over time. The satellite circles Earth’s poles and passes over the same spots at the same local solar time each day, making it ideal for monitoring changes in landscapes, weather patterns, and more.
KOMPSAT-7: Next-Generation Capabilities
KOMPSAT-7 is designed as one of the world’s most advanced ultra-high-resolution optical satellites. Built by the Korea Aerospace Research Institute, this satellite is the successor to KOMPSAT-3A (launched in 2015) and will provide detailed imagery of the Korean Peninsula and beyond.
Key features include:
- High-resolution imaging: Providing unprecedented detail for Earth observation.
- Real-time processing: The satellite is equipped with onboard storage and electro-optical modules to handle large volumes of imagery quickly.
- Optical data transmission: A first for Korean satellites, allowing for faster and more efficient data delivery.
Vega C Rocket Performance
This launch (VV28) was the sixth mission for the Vega C, a medium-lift rocket developed by the European Space Agency. While the program has seen five successful launches, one failure occurred in December 2022, highlighting the inherent risks of space travel.
The success of this mission demonstrates South Korea’s growing investment in space technology and its ability to secure reliable access to high-quality Earth observation data.
The deployment of KOMPSAT-7 signifies an important advancement in Korea’s remote sensing capabilities, enhancing its ability to monitor environmental changes, support national security, and provide critical information for a wide range of applications.